In a significant stride towards advancing cloud computing technology, both Google and Intel have recently unveiled their latest endeavors in custom chip development, introducing the Axion and Gaudi 3 processors, respectively. These developments underscore a pivotal shift towards self-reliance and innovation within the tech giants, as they aim to reduce dependency on traditional microprocessor manufacturers such as Nvidia, which has long held a dominant position in the data center processor market.

At its Cloud Next conference in Las Vegas, Google announced its custom ARM processor, named Axion, designed to enhance the efficiency and performance of its data centers. Built on ARM’s advanced Nanovers V2 technology, the Axion chip represents Google’s foray into custom server processors, aiming to boost the operational capabilities of its cloud services significantly. ARM technology is notable for its widespread adoption in mobile devices, with the company’s designs powering most premium smartphones. Google’s move to adopt ARM’s technology for its data center operations marks a significant step towards optimizing energy efficiency and computing power in cloud infrastructures.
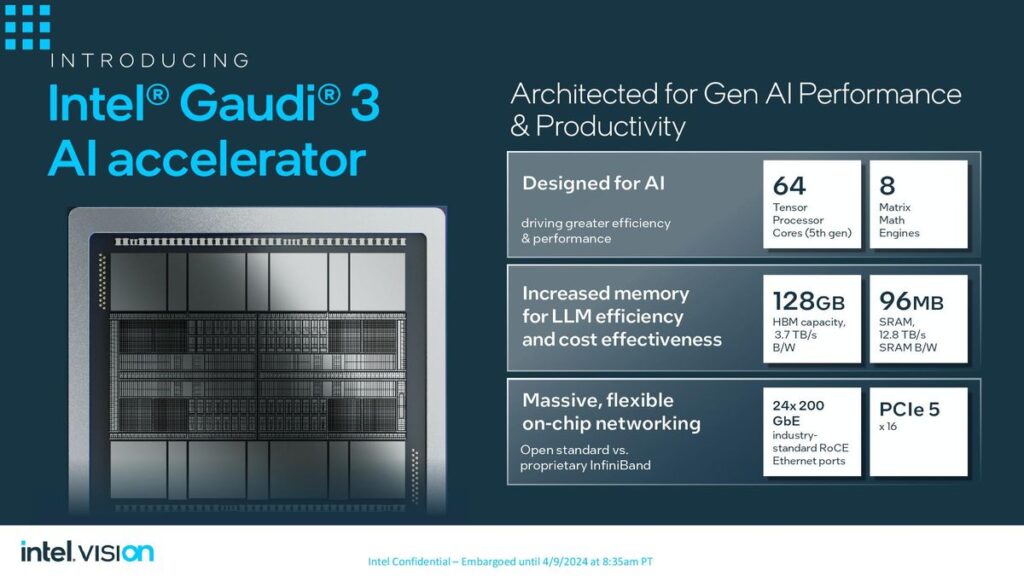
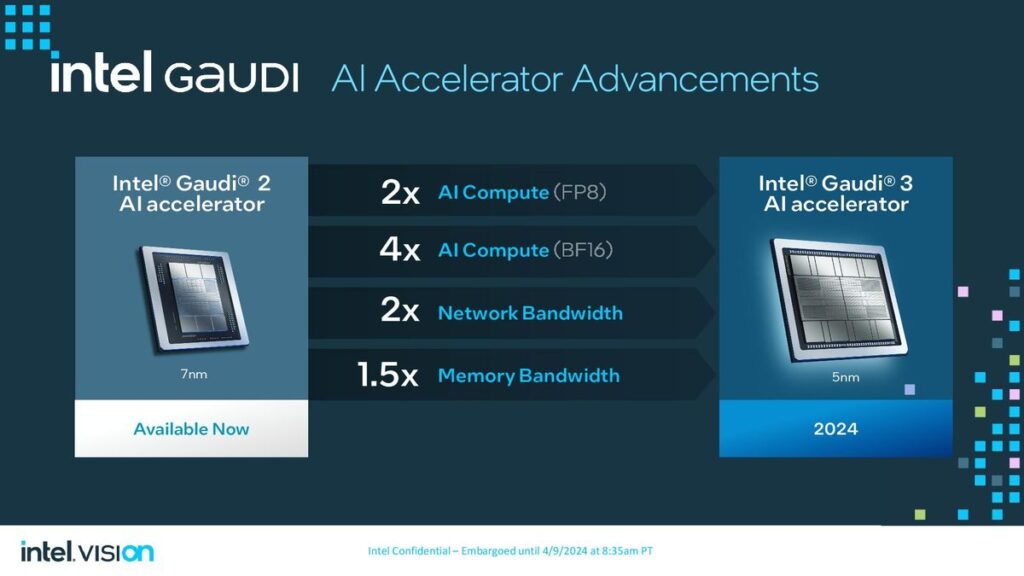
On the other hand, Intel revealed details of its new artificial intelligence (AI) chip, Gaudi 3, alongside its announcement of an ARM-based central processing unit for data centers. The Gaudi 3 AI processor, presented at Intel’s Vision event, is designed to accelerate AI workloads, offering a compelling alternative to Nvidia’s AI chips. Intel claims that the Gaudi 3 chip can train specific large language models up to 50% more quickly than Nvidia’s prior-generation H100 processor, emphasizing its potential to impact the AI computing landscape significantly.
Google’s Axion processor is touted to offer 30% better performance compared to the fastest general-purpose ARM-based virtual machines currently available and up to 50% better performance alongside 60% improved energy efficiency when compared to comparable VMs based on x86 architecture. The Axion chip is geared to support a wide array of computing workloads, ranging from web serving and data analytics to containerized workloads and databases, demonstrating Google’s ambition to cater to internal and external cloud computing needs.
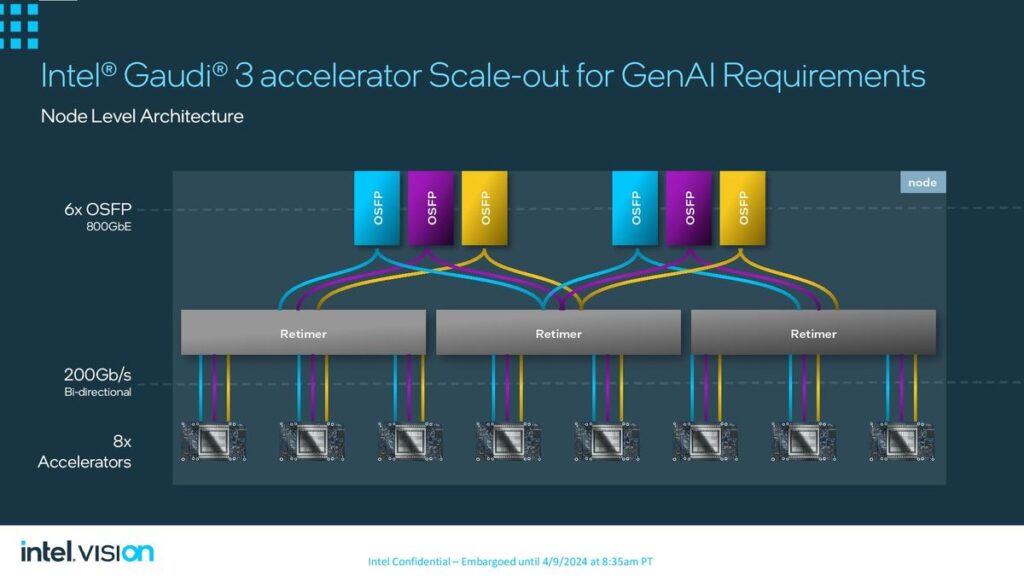
Similarly, Intel’s Gaudi 3 aims to provide a robust solution for AI workloads, leveraging a 5-nanometre process technology to enhance performance and efficiency. The Gaudi 3 includes two main processor chips fused, promising more than twice the speed of its predecessor and capable of being integrated into larger compute clusters for substantial AI processing power
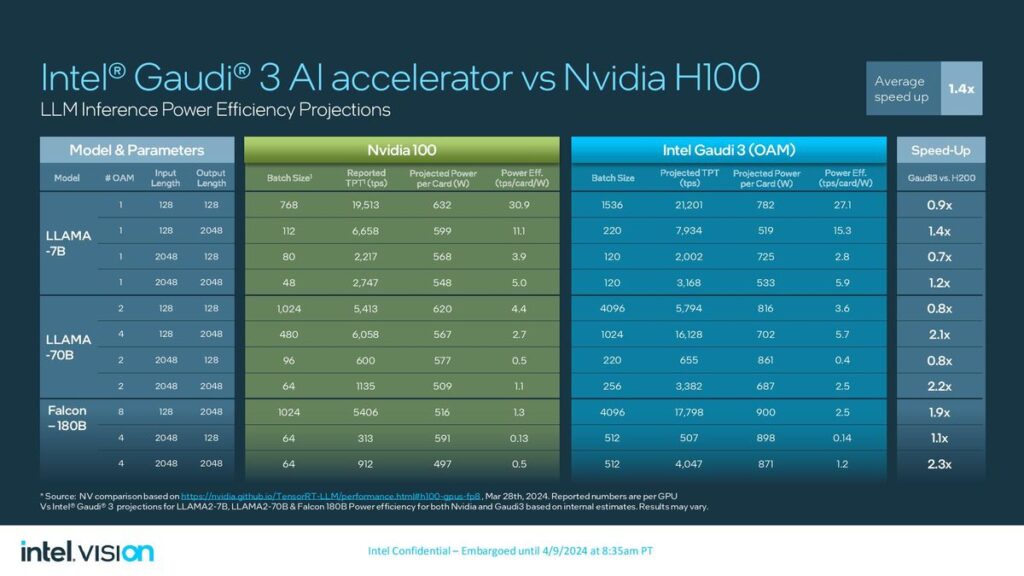
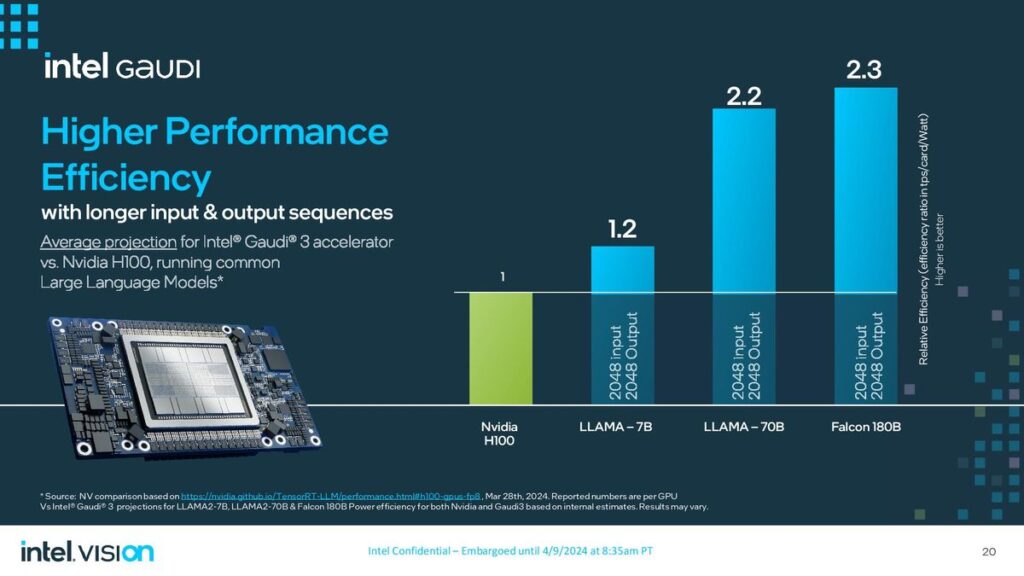

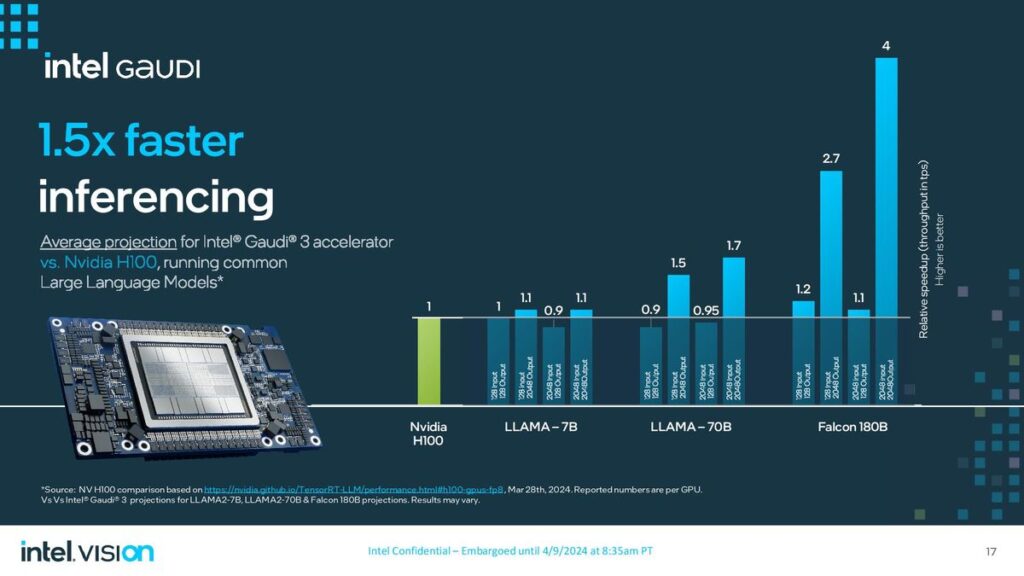
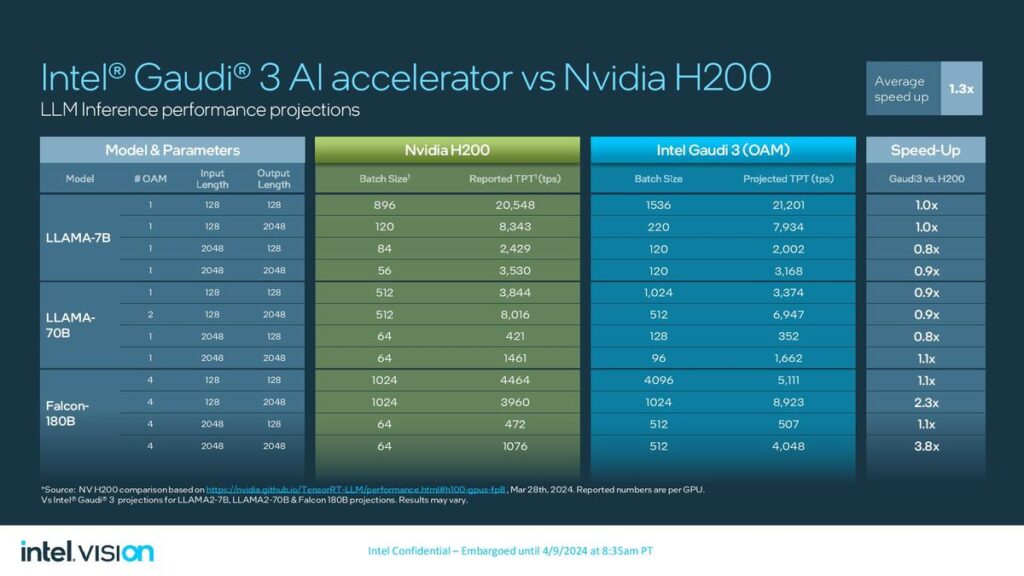
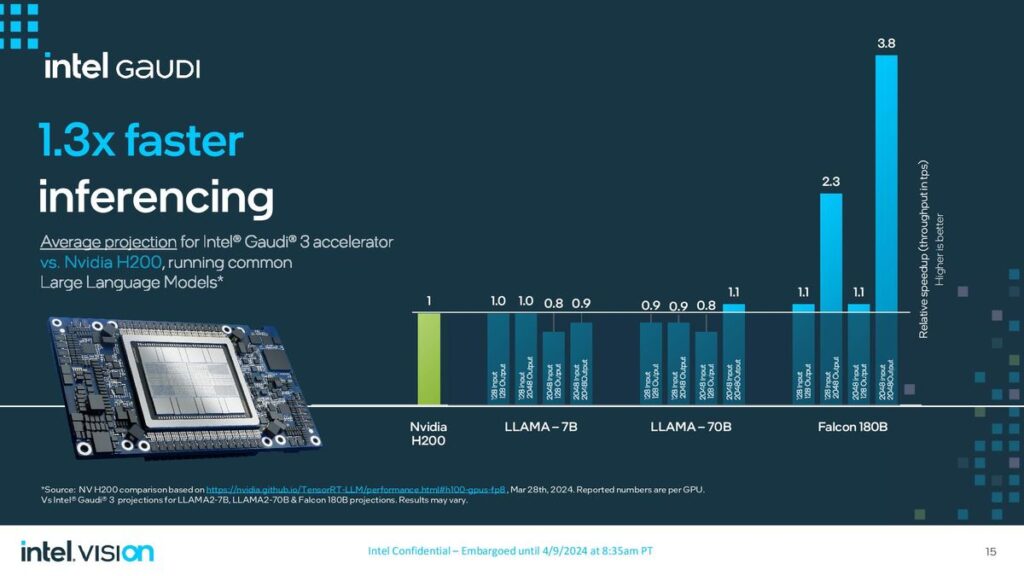
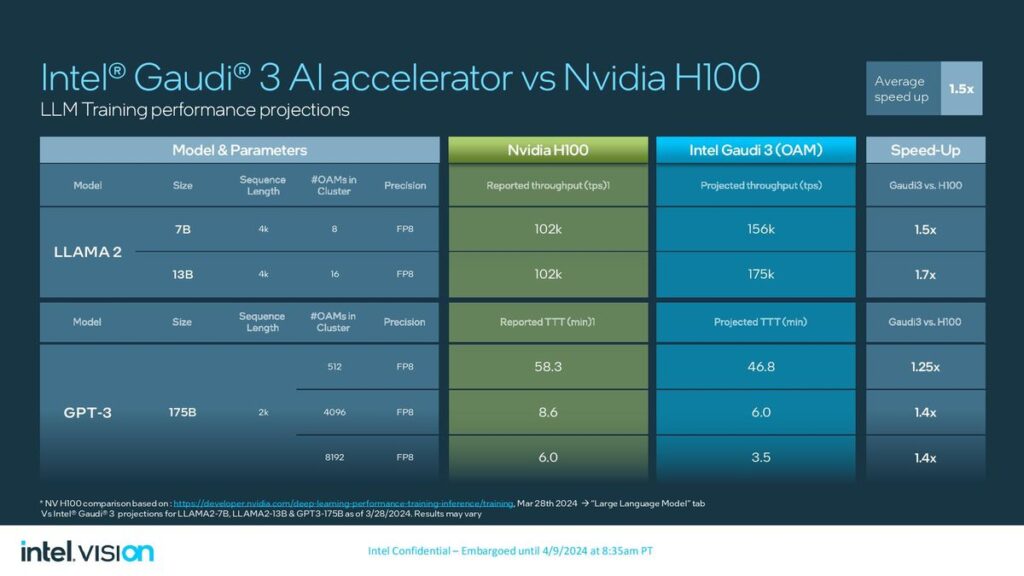
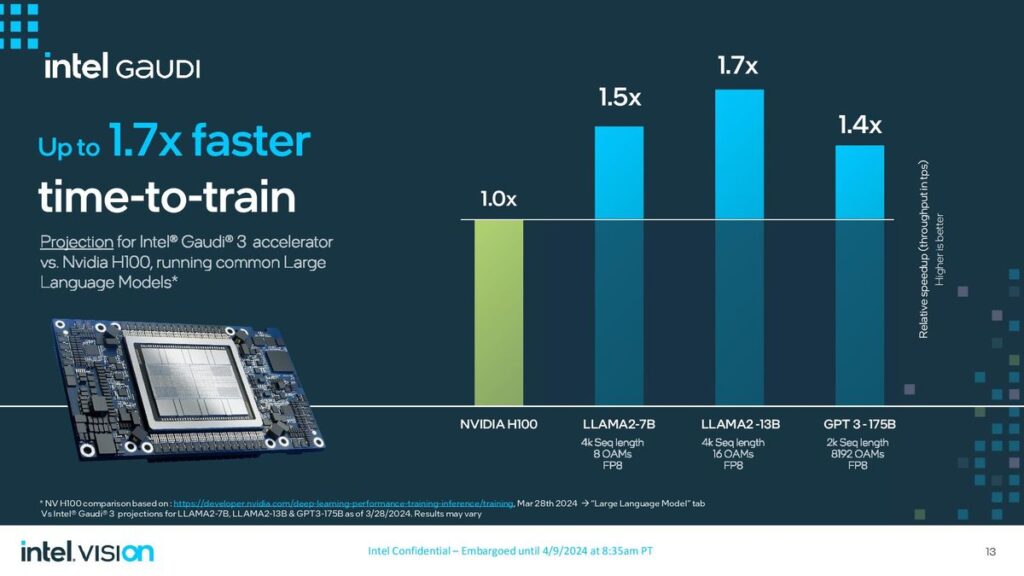
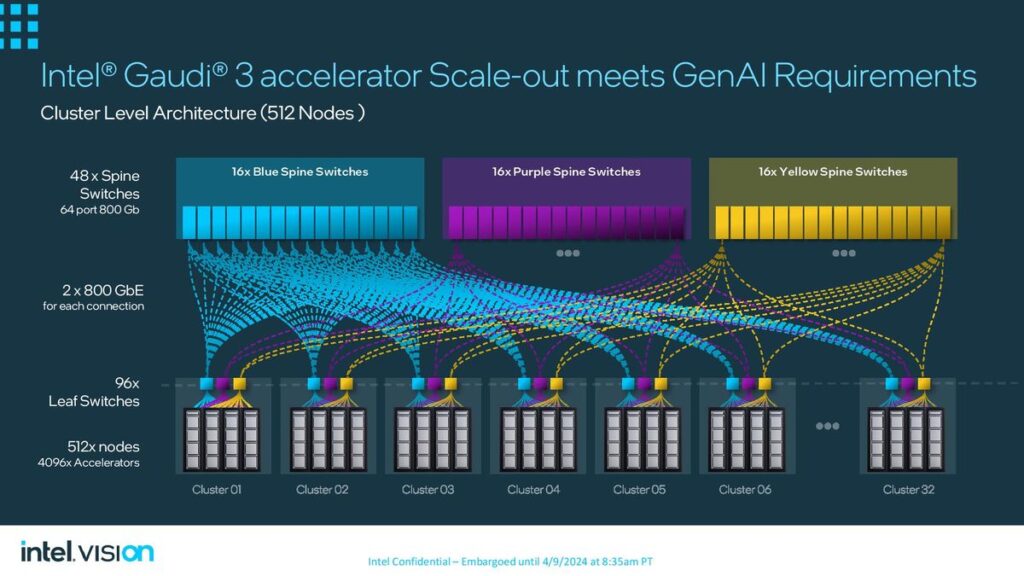



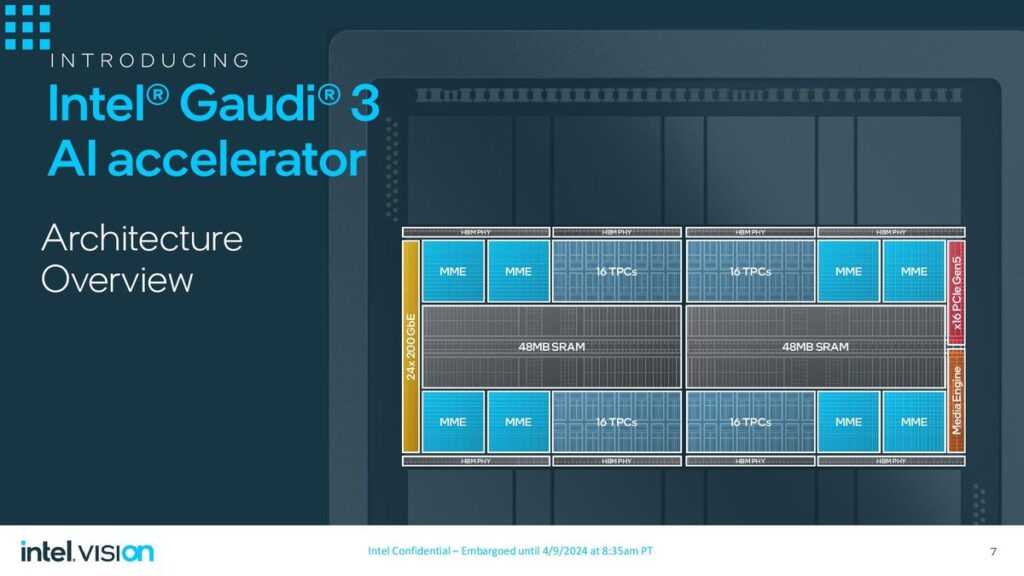








Google and Intel have strategically positioned their new processors as competitive alternatives to Nvidia’s offerings in the data center and AI markets. While Google’s Axion processor advances its cloud infrastructure capabilities, focusing on performance and energy efficiency, Intel’s Gaudi 3 processor aims to carve a niche in the rapidly growing field of AI computing, providing an alternative that emphasizes speed and efficiency in training large language models.
As the tech industry anticipates the wider adoption and deployment of these processors, the impact of Google’s Axion and Intel’s Gaudi 3 on the competitive dynamics of the cloud computing and AI markets remains to be fully realized. These developments signify the tech giants’ push towards innovation and self-reliance and herald a new era of competition and technological advancement in cloud computing and artificial intelligence.
Like this article? Keep up to date with AI news, apps, tools and get tips and tricks on how to improve with AI. Sign up to our Free AI Newsletter
Also, come check out our free AI training portal and community of business owners, entrepreneurs, executives and creators. Level up your business with AI ! New courses added weekly.
You can also follow us on X